Physics Model Question Paper – I
CBSE SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER
Grade : CLASS 11 Subject: PHYSICS Marks: 70
Time : 3hrs
General Instructions:
a) All the questions are compulsory.
b) There are37 questions in total.
c) This question paper contains four sections: Section-A, Section-B, Section-C and Section-D
d) Section-A contains 20 questions of one mark each.
e) Section-B contains 7 questions of two marks each.
f) Section-C contains 7 questions of three marks each.
g) Section –D contains 3 questions of five marks each.
SECTION – A
- Special theory of relativity explained by a)Thomas Alva Edison b) Ampere
c) Albert Einstein d) C V Raman
2. Among the given following units which one is the longest unit of length?
a) Angstrom b) Fermi
c) Barn d) Parsec
3. Dimensional formula of universal gravitational constant______________
a) MLT-2 b) ML-1T-2
c) M-1LT-2 d) None of the above
4. What is the angle between i and j ____________
a) b)
c)
d)
5. Which of the following statement is not true regarding the Newton’s third law of motion?
a) To every action there is always an equal and opposite reaction
b) Action and reaction act on the same body
c) There is no cause-effect relation between action and reaction
d) Action and reaction forces are simultaneous
6. For ‘n’ particles in a space, the suitable, the suitable expression for the x-coordinate of the centre of mass of the system is
a) b)
c)
d)
7. What happens when angular velocity of the Earth increases?
a) Acceleration due to gravity decreases at the equator
b) Acceleration due to gravity increases at the equator
c) moment of inertia of the earth increases
d) None of the above
8. Elasticity of a material can be altered by
a) annealing b) hammering
c) adding impurities d) all of the above
9. The amount of heat that a body can absorb by radiation___________
a) depends on colour of body only
b) depends on temperature of body only
c) depends on colour and temperature of body only
d) depends on density of body
10. The average energy associated with three translational degree of freedom is ________
a) b)
c) d)
11. Dimensional formula of viscosity is _______________
12. Two masses of 1g and 4g are moving with equal kinetic energy. The ratio of the magnitudes of
their velocity is _____________
13. Orbital velocity of satellite on the surface of earth is approximately _______________ km/s
Or
1 atmosphere = ________________________ N/m2
14. The efficiency of Carnot engine working between sink and source of temperatures 100k and 400k is ___________________
15. A simple harmonic motion is represented by metre. Its frequency of the wave is _________________ metre.
16. What is the relation between initial velocity of the projectile and time of flight?
17. Define Rigidity’s modulus of elasticity.
18. What happens to frequency of the pendulum when it taken to the top of a mountain.
Or
A force of 5N acts on a body for 2 milli sec. If the mass of the body is 5g, calculate the change in
momentum.
19. Define first law of thermodynamics.
20. Write the differences between longitudinal and transverse waves.
SECTION – B
21. What is the moment of inertia along a tangent of sphere of mass m and radius R. Give the factors affecting the moment of inertia of the body.
22. Two stones are falling at a place from heights in the ratio 2.3 what is the ratio of their velocities
on reaching the ground.
23. The angular velocity of a wheel increases from 120 to 480 rpm in 10sec. The number of revolutions made during this time is?
Or
Derive the expression for Kinetic energy of a body vibrating in SHM.
24. The average depth of Indian Ocean is about 3000 m. Calculate the fractional compression, of water at the bottom of the ocean. (given bulk modulus of water is 2.2 x 109 Nm-2 & g =10 ms-2)
Or
Derive an expression work done in isothermal process. And Discuss the internal energy change in isothermal process and adiabatic process .
25. State and explain Kepler’s laws of planetary motion. And explain why hydrogen is in abundance around the sun but not around earth?
26. What A liquid takes 3 minutes to cool from 800C to 600C. How much time will it take to cool from 600C to 400C? The temperature of the surroundings is 200C.
27. Define
a) Mean free path
b) Explain the effect of pressure of the gas and diameter of the molecule on mean free path.
SECTION – C
28. a) A lift is accelerated downward. Will the weight of the person inside the lift increase, decrease or remain the same?
b) If the lift is going up with uniform speed, then?
c) Explain about variation of g with height and depth.
29. Derive
a)
b) A function is defined as
where ‘
’ is the angle, measured in radians. Write the dimensional formula for
.
30. State and prove perpendicular axis theorem. What is moment of inertia for a circular disc of radius R and mass M along tangent perpendicular to its diameter?
31. Describe the behaviour of a wire under gradually increasing load.
Or
A metal rod of young’s modulus undergoes an elastic strain of 0.006.Then what is the energy per unit volume stored in
32. a) Define inertia and explain different types of inertia with examples.
b) If a table is to be taken from one corners of a room to another corner which is better pulling or pushing? Explain.
33. a) State and prove work-Energy theorem. b) Give the units and dimensions for co-efficient of restitution.
34. A spring mass system is executing simple harmonic motion as shown below.
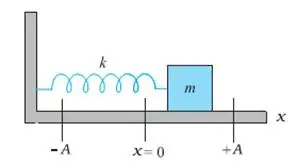
For this system
- Write a general equation for the displacement, as a function of time.
- Using the above equation, find the equations for velocity and acceleration.
c. Plot graphs showing the variations of displacement ‘x’, velocity ‘v’ and acceleration ‘a’ as a function of time.
SECTION – D
35. a. Explain about Young’s modulus and give the experimental details to measure the Young’s modulus of a material wire.
b. If an iron wire is stretched by 1%, what is the strain on the wire?
Or
c. What is Doppler Effect? Obtain an expression for the apparent frequency heard by the
observer in case of source is moving towards the observer and observer at rest.
d. Discuss about harmonics formed in a closed pipe.
36. a. Define adiabatic process. Obtain the expression for work done in an adiabatic process.
b. Why a heat engine with 100% efficiency can never be realized in practice? Explain with the help of Carnot’s engine efficiency expression.
Or
c. State Bernoulli’s theorem for an incompressible fluid.
d. With a neat sketch, explain how one can measure the flow speed of incompressible fluid. Give an equation for flow speed.
37. a. Prove that the path of a projectile is a parabola.
b. Give the properties of dot product and give one example.
Or
a. Two balls A and B on a horizontal surface. Initially ball B is at rest and ball A is moving with speed u along a line joining the centers of the balls.
The mass of the balls are mA and mB.
Using the law of conservation of linear momentum and law of conservation of kinetic energy, obtain the equations for velocity of ball A and ball B.
***ALL THE BEST ***
Download – Physics Model Question Paper – I