Magnetism and Matter Questions
For Electric Charges and Fields Questions: CLICK HERE
1 Mark Questions:
- Write the equations for magnetic field due to a bar magnet at it’s
- Axial point and
- Point on equatorial plane.
- Write any four properties of magnetic field lines.
- Relative permeability of a material is µr = 0.5. Identify the nature of the magnetic material and write its relation of magnetic susceptibility.
- What are permanent magnets? Give one example.
- When on the surface of earth is the vertical component of earth’s magnetic field zero?
- The horizontal component if earth’s magnetic field at a place s B and angle of dip is 60o. What is the value of the vertical component of the earth’s magnetic field?
- What is the angle of dip at a place where the horizontal and vertical components of the earth’s magnetic field are equal?
- A magnetic needle free to rotate in a vertical plane orients itself vertically at a certain place on the earth. What are the values of a) Horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field and b) Angle of dip at this place.
- Where on the surface of earth, is the angle of dip 90o?
- The permeability of a magnetic material is 0.9983. Name the type of magnetic material, it represents.
- The susceptibility of a magnetic material is 1.9 x 10-5. Name the type of magnetic material, it represents.
- If the horizontal component and vertical components of the earth’s magnetic field are equal at a certain place, what would be the angle of dip at that place?
- What is the characteristic property of a diamagnetic material?
- Define the term magnetic declination.
- What is the characteristic property of a paramagnetic material?
- How the ferro magnetic material does behave on heating?
- How the Para magnetism depends on the temperature?
- In superconducting state, write the magnetic characteristics of a conductor.
2 Mark Questions:
- Draw the magnetic field lines due to a current passing through a long solenoid. Use Ampere’s circuital law, to obtain the expression for the magnetic field due to the current I in a long solenoid having n number of turns per unit length.
- Two long straight parallel conductors a and b carrying steady currents Ia and Ib respectively are separated by a distance d. What is the nature and magnitude of the force between the two conductors?
- Show with the help of a diagram, how the force between the two conductors would change when the currents in them flow in the opposite directions.
- A circular coil of N turns and radius R carries a current I. It is unwound and rewound to make another coil of radius R/2, current I remaining the same. Calculate the ratio of the magnetic moments of the new coil and the original coil.
- A circular coil of N turns and diameter d carries a current I. It is unwound and rewound to make another coil of diameter 2d, current I remaining the same. Calculate the ratio of magnetic moments of the new coil and the original coil.
- Explain the following:
- Why does magnetic lines of force form continue closed loops?
- Why are the field lines repelled(expelled) when a diamagnetic material is placed in an external uniform magnetic field?
- A small compass needle of magnetic moment M and moment of inertia Imis free to oscillate in a magnetic field B. It is slightly disturbed from its equilibrium position and then released. Show that it executes simple harmonic motion. Hence, write the expression for its time period.
- How a circular loop carrying current does behaves as a magnet?
- Deduce the expression for the magnetic dipole for the magnetic dipole moment of an electron orbiting around the central nucleus.
- State Gauss’s law of magnetism. Explain why magnetic monopoles do not exist.
- Show diagrammatically the behaviour of magnetic field lines in the presence of
- Paramagnetic and
- Diamagnetic substances. How does one explain this distinguishing feature?
- Out of the two magnetic materials, A has relative permeability slightly greater that unity while B has slightly less than unity. Identify the nature of the materials A and B. Will their susceptibilities be positive or negative?
- Give two points to distinguish between a paramagnetic and diamagnetic substance.
- Explain:
- How an electromagnet is different from a permanent magnet?
- Write two properties of a material which makes it suitable for making electromagnet.
- The relative magnetic permeability of a magnetic material is 800. Identify the nature of magnetic material and state its two properties.
- Explain:
- How does a diamagnetic material behave when it is cooled to very low temperature?
- Why does a paramagnetic sample display greater magnetization when cooled?
- A magnetic needle free to rotate in a vertical plane parallel to the magnetic meridian has its North tip down at 60owith the horizontal. The horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field at that place is known to be 0.4 G. Determine themagnitude of the earth’s magnetic field at the place.
- Distinguish between diamagnetic and ferromagnetic materials in terms of
- Susceptibility and
- Their behaviour in a non-uniform magnetic field.
- Answer the following questions.
- Write two characteristic properties of a material used for making permanent magnets?
- Why is core of an electromagnet made of soft ferromagnetic materials?
- The horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field at a place is 1.732 times its vertical component there. Find the value of angle of dip at that place. What is the ratio of the horizontal component to the total magnetic field of the earth at that place?
- The horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field at a place is equal to its vertical component there. Find the value of angle of dip at that place. What is the ratio of the horizontal component to the total magnetic field of the earth at that place?
- Draw the magnetic field lines when a i. diamagnetic material and ii. Paramagnetic material is placed in an external magnetic field. Which magnetic property distinguishes this behaviour of the field lines due to the two substances?
- State briefly an efficient way of making a permanentmagnet. Write two properties to select suitable material for making permanent magnets.
- Out of the following, identify the material which can be classified as
- Paramagnetic and
- Diamagnetic.
- Aluminium
- Bismuth
- Copper
- Sodium. Write one property to distinguish between paramagnetic and diamagnetic materials.
- Define magnetic susceptibility of a material. Name two elements one having positive susceptibility and the other having negative susceptibility. What does negative susceptibility signify?
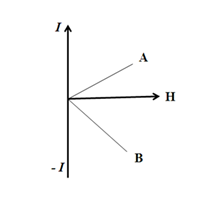
- Draw a plot showing the variation of intensity of magnetization with the applied magnetic field intensity fir bismuth. Under what condition does a diamagnetic material exhibit perfect conductivity and perfect diamagnetism?
- The following figure shows the variation of intensity of magnetization (I) versus the applied magnetic field intensity (H) for two magnetic materials A and B. a) Identify the materials A and B. b) Why does the material B have a larger susceptibility that A for a given field at constant temperature?
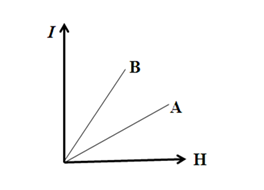
28. The following plot shows the variation of intensity of magnetization I versus the applied magnetic field intensity H for two magnetic materials A and B.
- Identify the materials A and B.
- Draw the variation of magnetic susceptibility χmwith temperature for B.
3 Mark Questions:
- A wheel with 8 metallic spokes each of 50 cm long is rotated with a speed of 120rev/min in a plane normal to the horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field. The earth’s magnetic field at the place is 0.4 G and the angle of dip is 60o. Calculate the emf induced between the axle and the rim of the wheel. If the number of spokes were increased, how does the emf be affected?
- Name and define the two elements of the earth’s magnetic field other than the horizontal component. Why do we say that the places like Delhi and Mumbai, a magnetic needle shows the true North direction quite accurately as compared to other places in India?
- Three identical specimens of a magnetic materials nickel, antimony and aluminiumare kept in a non-uniform magnetic field. Draw the modification in the field lines in each case. Justify your answer.
- Answer the following questions. a) What happens when a diamagnetic substance is placed in a varying magnetic field? b) a core of an electromagnet
- Name the three elements required to specify the earth’s magnetic field at a given place. Draw a labelled diagram to define these elements. Explain briefly how these elements are determining to find out the magnetic field at a given place on the surface of the earth.
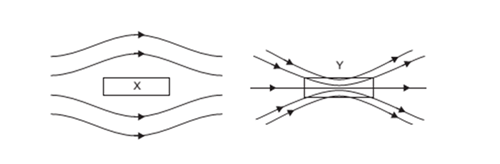
- Answer the following questions. a) How does angle of dip change as one goes from magnetic pole to magnetic equator of the Earth? b) A uniform magnetic field gets modified as shown below when two specimens X and Y are placed in it. Identify whether specimens X and Yare diamagnetic, paramagnetic or ferromagnetic.
5 Mark Question:
- Answer the following questions. a) A small compass needle of magnetic moment ‘m’ is free to turn about an axis perpendicular to the direction of uniform magnetic field ‘B’. The moment of inertia of the needle about the axis is ‘I’. The needle is slightly disturbed from its stable position and then released. Prove that it executes simple harmonic motion. Hence deduce the expression for its time period. b) A compass needle, free to turn in a vertical plane orients itself with its axis vertical at a certain place on the earth. Find out the values of a) horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field and b) angle of dip at the place.