Physics Class 11 Model Question Paper – II
Grade : XI Subject: PHYSICS Marks: 70
Time : 3hrs
General Instructions:
a) All the questions are compulsory.
b) There are37 questions in total.
c) This question paper contains four sections: Section-A, Section-B, Section-C and Section-D
d) Section-A contains 20 questions of one mark each.
e) Section-B contains 7 questions of two marks each.
f) Section-C contains 7 questions of three marks each.
g) Section –D contains 3 questions of five marks each.
SECTION – A
- The Raman effect deals with a) Diffraction of light with medium particles b) refraction of light with medium particles
c) Scattering of light with medium particles d) reflection of light by medium particles
2. Among the given following units which one is not unit of length?
a) Angstrom b) Fermi
c) Barn d) Parsec
3. Moment of inertial depends upon______ of the body
- mass b) shape
c) temperature d) all the above
4. If then the angle between
is____________
a) b)
c) d)
5. Which of the following statement is not true regarding the Newton’s third law of motion?
a) To every action there is always an equal and opposite reaction
b) Action and reaction act on the same body
c) There is no cause-effect relation between action and reaction
d) Action and reaction forces are simultaneous
6. For ‘n’ particles in a space, the suitable, the suitable expression for the x-coordinate of the centre of mass of the system is
a) b)
c) d)
7. Earth is flattened at the poles and bulges at the equators. This is due to the fact that_______
a) the revolves around the sun in an elliptical orbit
b) the angular velocity of spinning about its axis is more at the equator
c) the centrifugal force is more at the equator than an poles
d) None of the above
8. The co-efficient of viscosity for hot air is ___________
- Greater than the co-efficient of viscosity for cold air
- Smaller than the co-efficient of viscosity for cold air
- Same as the co-efficient of viscosity for cold air
- Increases (or) decreases depending on external pressure
9. The amount of heat that a body can absorb by radiation___________
a) depends on colour of body only
b) depends on temperature of body only
c) depends on colour and temperature of body only
d) depends on density of body
10. The average energy associated with each translational degree of freedom is ________
a) b)
c) d)
11. Dimensional formula of power is _______________
12. Two masses of 1g and 4g are moving with equal kinetic energy. The ratio of the magnitudes of
their momentum is _____________
13. Escape velocity on the surface of earth is ________________ km/s
Or
1 atmosphere = ________________________ N/m2
14. The efficiency of Carnot engine working between boiling point and freezing point of water is
_______________
15. A simple harmonic motion is represented by metre. Its amplitude is
_________________ metre.
16. What is the relation between horizontal range and angle of projection?
17. Define Young’s modulus of elasticity for perfectly rigid body.
18. What happens when pendulum clock taken to the top of a mountain.
Or
A force of 5N acts on a body for 2 milli sec. If the mass of the body is 5g, calculate the change in velocity.
19. Define zeroth law of thermodynamics.
20. Draw the graph between displacement and time which represents uniform velocity.
SECTION – B
21. State and explain Kepler’s laws of planetary motion.
22. Two stones are falling at a place from heights in the ratio 2.3 what is the ratio of their velocities
on reaching the ground.
23. In 20 seconds, the speed of a motor changes from 1200 rpm to 1800 rpm. In this period of time, the number of revolutions completed by it is?
Or
Derive the expression for Kinetic energy of a body vibrating in SHM.
24. Calculate the fractional change in volume of a glass slab, when subjected to a hydraulic pressure
of 10 atmosphere (Bulk modulus) of elasticity of glass is )
Or
Give the differences between isothermal process and adiabatic process.
25. State and prove perpendicular axis theorem.
26. What is specific heat? Give its units.
27. a) Define mean free path
b) Write the factors affecting the mean free path.
SECTION – C
28. Explain graphically the variation of displacement, velocity & acceleration with time for a
particle in SHM..
29. a. Show that S = ut + ½ at2.
b. Draw the graphs for i) Uniform velocity ii) Rest
30. Explain about cross product, write the properties of cross product and give any one examples of a physical quantity which can be expressed as cross product of two physical quantities. Give one more example of a physical quantity which can be expressed as dot product of two physical quantities.
31. Describe the behaviour of a wire under gradually increasing load with necessary graph.
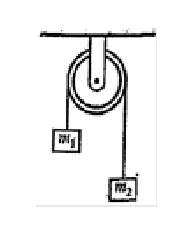
32. Two masses tied to a string are hanging over a light frictionless pulley. What is the acceleration of the masses, when left free to move? Given: g=9.8 ms-2.
33. a) State and prove work-Energy theorem.
b) Give the units and dimensions for co-efficient of restitution.
34. Show that the orbital velocity of a satellite is independent of mass of the satellite.
Or
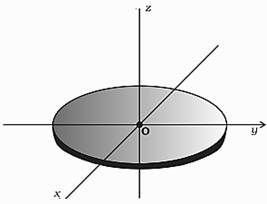
State the theorem of perpendicular axes. Give the expression with respect to the diagram
What is the moment of inertia of a disc about one of its diameters and along Z-axis?
(M-Mass of the disc and R-Radius of the disc)
SECTION – D
35. a) State the parallelogram law of vectors. Derive an expression for the magnitude of the resultant
vector.
- The vector A has a magnitude 5 unit, B has a magnitude of 6 unit and the cross product A and
B has the magnitude of 15 unit. Find the angle between A and B.
Or
- Define rolling friction and give the laws of rolling friction.
- Mention the methods used to decrease friction.
- A vehicle of mass 120kg is moving with a velocity of 90kmph. What force should be applied on the vehicle to stop it in 5 sec?
36. a) State and prove Bernoulli’s principle.
b) What is Torricelli’s law? Derive an expression for the speed of efflux with an experiment.
Or
a) Define Head on collision and derive the expressions for the final velocities of bodies after one
dimensional elastic collision between two bodies.
b) A simple pendulum in a stationary lift has time period T. What would be the effect on the T when the lift a) Moves up with uniform velocity b) Moves down with uniform acceleration.
37. a) What is Doppler’s effect? Derive the expression for an apparent frequency when the source is moving towards a stationary observer.
b) A 10m long steel wire has mass 5g. If the wire is under tension of 80N, then calculate the
speed of transverse waves.
Or
- Derive the expression for work done in isothermal process.
- Derive the relation between the two specific heat capacities of a gas on the basis of first law of
thermo dynamics.
* * *